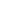In times of high competition and high market saturation, one way to increase efficiency and improve the quality of production is to optimise production processes. Optimisation of production processes consists of adjusting production processes so that they are more effective, also leading to increased performance, cost reduction and improvement of product quality. Thanks to the optimisation of production processes, enterprises can adapt to changing market conditions and customer demands, often requiring producing high-quality products in short time.
This article will present the benefits of optimising production processes and best practices in the field of optimisation. Examples of tools and methods that can be used to optimise production processes will be discussed, among others, in relation to the automation, monitoring and analysis of production processes and the use of data to adapt production to changing market conditions.
The process of production optimisation in various business ventures may encompass numerous aspects:
Production Process Analysis involves making a thorough assessment of each stage of the process to identify areas where performance or product quality can be increased. As part of the analysis of production processes, it is worth paying attention to process mapping, which consists of a thorough understanding of the sequence of activities, operations and stages that occur in the production process and their graphical representation.
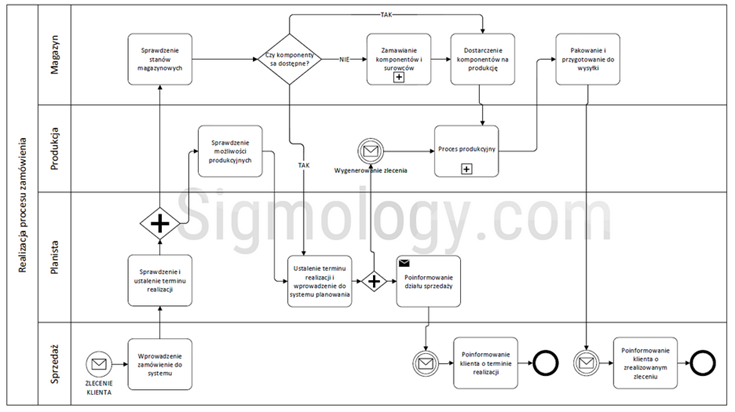
Fig. 1 Map of the implementation of the order process, Source >>
Process automation involves the introduction of machines, robots, control and monitoring systems that perform production tasks with minimal or no human involvement. The main goal of automation of production processes is to increase efficiency, improve quality, reduce costs, shorten cycle time, and minimize the risk of errors. Automation can be employed in various areas of the production process, including material processing, assembly, quality testing, packaging, and logistics.
Monitoring and analysing processes can help identify trends and events that affect product performance or quality. This allows companies to take appropriate steps to adapt their processes to changing market conditions. It includes systematic data collection, observation, visualization, and reporting, as well as analysis of various parameters or indicators, and identification of non-conformities and problems, which allows us to obtain a full picture of the operation of processes and identify areas for improvement.
Production planning that aims to establish an optimal production schedule to meet market demand for products. This includes demand forecasting, capacity planning, coordination, and organisation of numerous factors such as availability of raw materials, production capacity, time, costs and priorities and monitoring and adaptation of the plan to ensure effective and efficient production.
What solutions should you implement?
In the process of production optimisation, it is extremely important to adapt production processes to changing market conditions. For this purpose, economic operators can use many tools and techniques, for example, Lean Manufacturing, Six Sigma or Total Quality Management.
Lean Manufacturing is a method of optimising production processes that focuses on eliminating losses and increasing added value in production processes, by limiting any activities that do not add value to the product but reduce costs and increase their innovation.
Six Sigma is a production process optimisation method that focuses on minimizing errors. This method, based on the analysis of production data and implementation of activities, is meant to reduce costs resulting from the production of defective products, i.e., costs of materials, working time, complaints, as well as image costs.
Total Quality Management (TQM) is a production process optimisation method that focuses on enhancing product and process quality by implementing quality control systems and actions to minimize production errors. It is an innovative method that promotes the building of a comprehensive, individual organizational culture of the enterprise based on common goals and values.
Implementations illustrate the multitude of opportunities
The above methods and techniques are used to optimise production processes and are used by enterprises all over the world. One example of the automation of production processes is the use of industrial robots. For example, General Motors uses the Fanuc R-2000iB in the process of vehicle assembly.
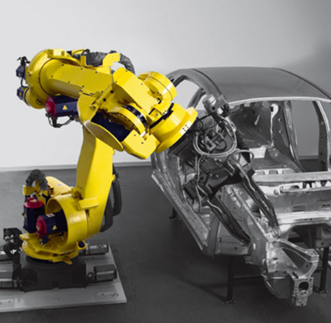
Fig. 2 An embodiment of the Fanuc R-2000iB robot for the production of motor vehicles, Source >>
In the medical, electronics and food industries, the KUKA KR AGILUS robot is often used. Thanks to its integrated energy supply system and proven control technology, it offers maximum precision in minimal space. For example, in Siemens AG, KUKA robots are used in the production of photovoltaic panels, and in a university clinic in the Danish city of Aalborg, the robot is used to automatically sort and control blood samples.

Fig. 3 KUKA KR robot in the use of the Clinic from Aalborg, Source >>
Another example of production process automation is the use of Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES). This system works in many areas and can have different degrees of complexity, but its primary task is to manage the collected production data. The MES system allows you to manage production processes in real time, from production planning and control to quality monitoring and resource management.
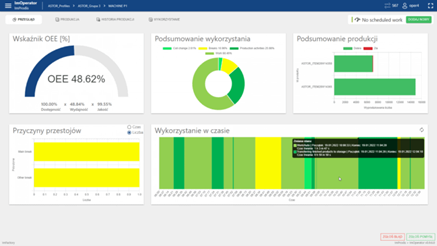
Fig. 5, MES system interface, Source >>
Profits in many areas of activity
The most important benefits of optimising production processes include increased production efficiency, which may mean the production of more units at the same time or maintaining the existing production at a lower cost. In addition, it reduces costs and eliminates losses resulting from excessive consumption of raw materials, excessive operations, or unnecessary downtime. The improvement of production processes can result in a shorter production cycle time, which means the ability to deliver products to customers in a shorter time while improving their quality, which can lead to increased satisfaction, greater customer loyalty and a positive brand image. Process optimisation also enables a more flexible production process, i.e., the ability to quickly adapt to changing market needs and demand. Importantly, optimisation of production processes can lead to improved working conditions and safety of employees, as it allows to identify risk areas and implement appropriate countermeasures to ensure a safe and healthy working environment. Thanks to better management of raw materials and finished products, we can minimize the costs associated with storing excessive quantities or avoid the risk of shortages.
Patent protection of the best solutions
Many such solutions are also patented, such as the solution known from US2014088748 A, which relates to the method of storing product units in storage or order-picking installation. Incoming goods loaded on pallets are temporarily stored in the store and delivered, if required, to a depalletization station, where they are stored individually in a buffer warehouse divided into product types. After this stage, the pallet is assembled with several types of products, according to the customer’s order. Then the mixed pallets for the individual industries are automatically set up, delivered to the delivery zone, and loaded onto the trucks.
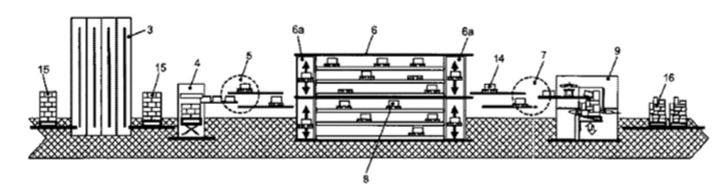
A similar solution is the one disclosed in US5636966A for an automated order-picking system consisting of known available components that also includes a system management computer based on accepted orders. The system allows you to divide the order into desired full pallets with many ordered layers of goods, which can be combined freely into full pallets depending on the submitted product order regarding both the number of products and their type.
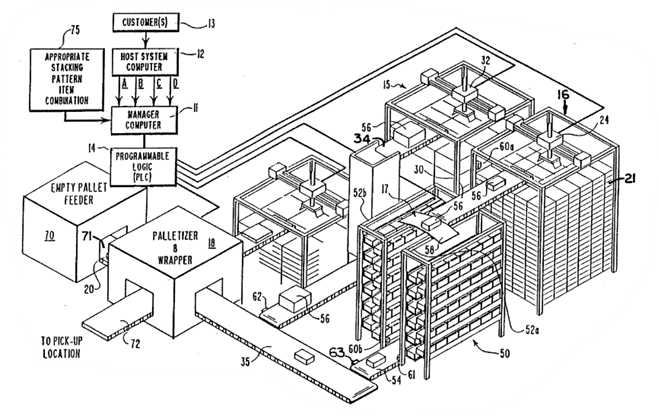
Optimisation of production processes is a key element of success for any manufacturing company. The implementation of optimisation methods and techniques, as well as automation and attention to aspects related to occupational safety and environmental protection, translates into increasing the efficiency, quality, and competitiveness of the company on the market. Reducing delivery time, lowering costs, increasing efficiency, and improving product quality enable a company to compete more effectively, win more customers, and increase its market share, which also means better quality for the recipients of individual products or services. Patent bases are a reliable source of knowledge about production processes, and the ability to protect your innovative solution, also in this area of activity, may be an additional source of high profits for the company. To this end, it is worth consulting an experienced patent attorney who can share market expertise and help reserve the right to proprietary solutions.